Experts on red alert for mega-earthquake off US coast - after analyzing a hole on a fault line - Daily Mail
4/15/23 at 3:00am
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Rare image of Uranus' rings captured by scientists through the James Webb Space Telescope - The Yucatan Times
4/15/23 at 3:01pm

The James Webb Space Telescope has taken a stunning image of Uranus that showcases 11 of the planet’s 13 rings. Made of rocks and dust that don’t reflect much sunlight, Uranus’ ri…
Viewed by
You are the first to view
How did the Andes Mountains get so huge? A new geological research method may hold the answer - Phys.org
4/15/23 at 3:01pm

How did the Andes—the world's longest mountain range—reach its enormous size? This is just one of the geological questions that a new method developed by researchers at the University of Copenhagen may be able to answer. With unprecedented precision, the meth…
Viewed by
You are the first to view
New Carl Sagan documentary in the works from National Geographic and Seth MacFarlane - Space.com
4/15/23 at 3:01pm
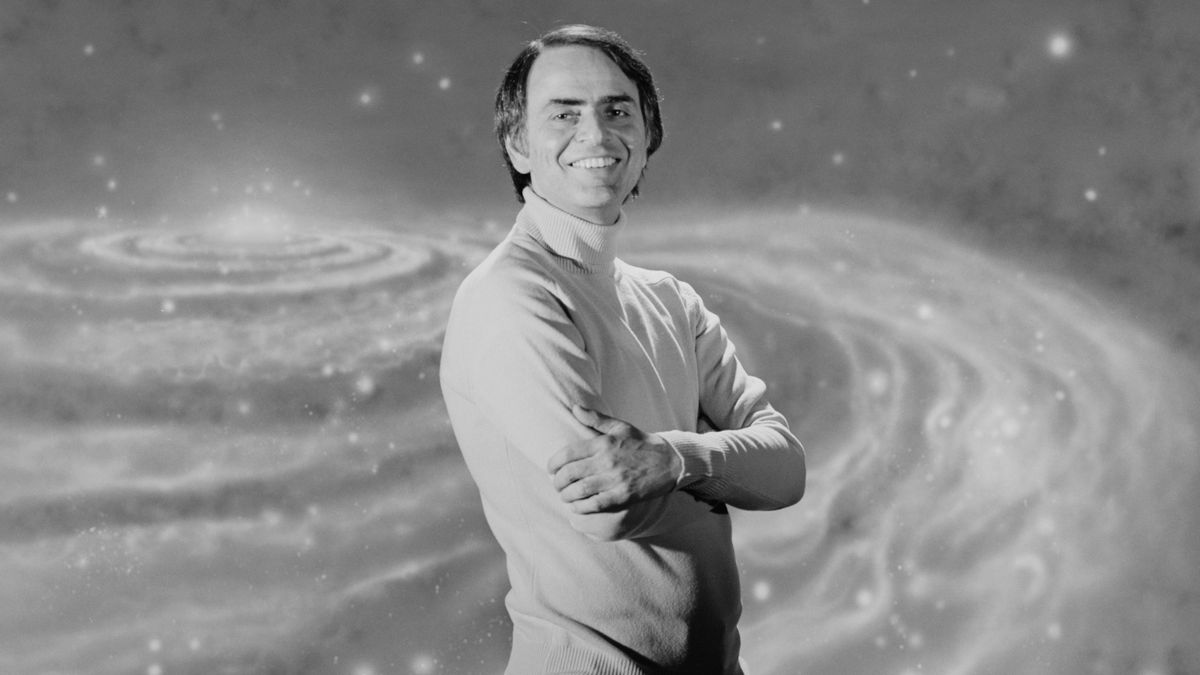

The 'Family Guy' and 'The Orville' creator unites with NatGeo to celebrate the famed astronomer.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Curious Rover captures dragon-like skeleton photo on Mars - KMPH Fox 26
4/15/23 at 3:01pm

NASA shared some bizarre images caputued by Mars rover
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Ancient inscription on jar found in Israel links kingdoms of Solomon and Sheba - Livescience.com
4/15/23 at 3:01pm
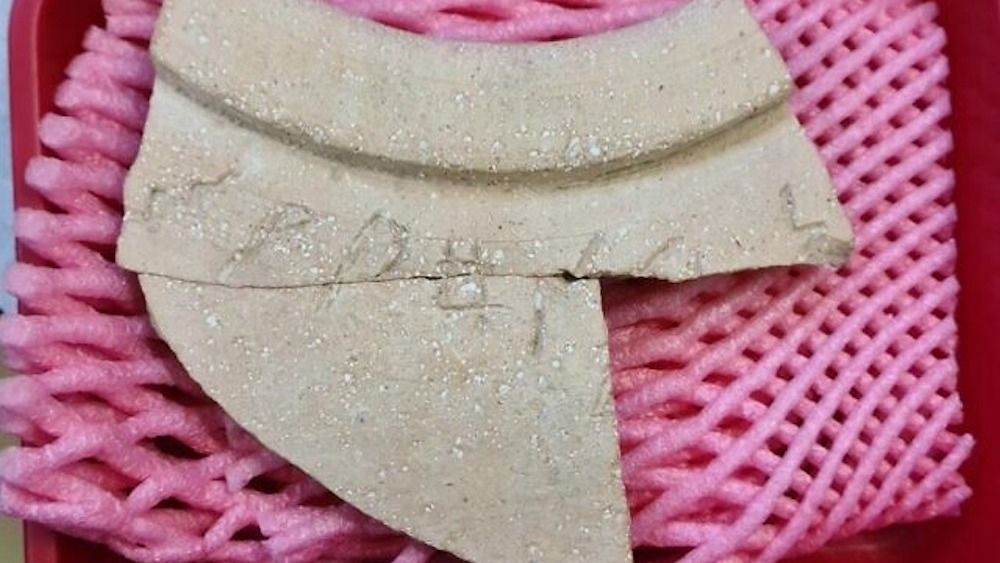

A new study has deciphered a mysterious inscription on a jar unearthed in Israel that lists an ingredient for making incense.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
NASA director takes oath on Carl Sagan’s Pale Blue Dot instead of Bible - The News International
4/15/23 at 3:00am
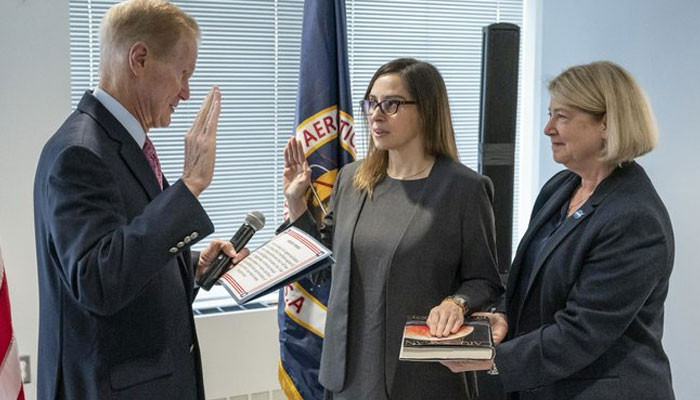

A newly-appointed top NASA officer Makenzie Lystrup swore an unconventional oath to take charge of her tasks.Rather than swearing an oath on the Bible, Makenzie Lystrup took her oath on a copy of...
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Accountants' tricks can help identify cheating scientists, says new study - Phys.org
4/15/23 at 3:01pm

Auditing practices from the finance industry can be adapted to identify academic fraud, according to new research by the University of St Andrews.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Daughter tries to explain to parents why the Mars Rover brings her to tears: ‘He’s a robot, why are you crying?’ - Yahoo Life
4/15/23 at 3:00am

"Every year that he was up there, he would sing 'Happy Birthday' to himself..."
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Museum searches for meteorite debris in N.B. worth $25K - CTV News
4/15/23 at 1:07am

A museum in Maine is offering $25,000 USD for a chunk of a meteor that fell in either Maine or New Brunswick last weekend.Subscribe to CTV News to watch more...
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Physicists lead experiments to explore the force that binds the universe - Phys.org
4/16/23 at 3:01am

The universe began about 14 billion years ago with a single point that contained a vast array of fundamental particles, according to the prevailing theory known as the Big Bang. Under the pressure of extreme heat and energy, the point inflated and then expand…
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Time Out: We All Need a Three-Day Weekend - Neuroscience News
4/15/23 at 3:00am

A three-day weekend is good for our health, a new study reports. An extra day of rest improves sleep duration, increases physical activity and was associated with overall healthier behaviors.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
NASA sets sights on a next-generation Mars helicopter to return Red Planet samples - Space.com
4/15/23 at 3:00am
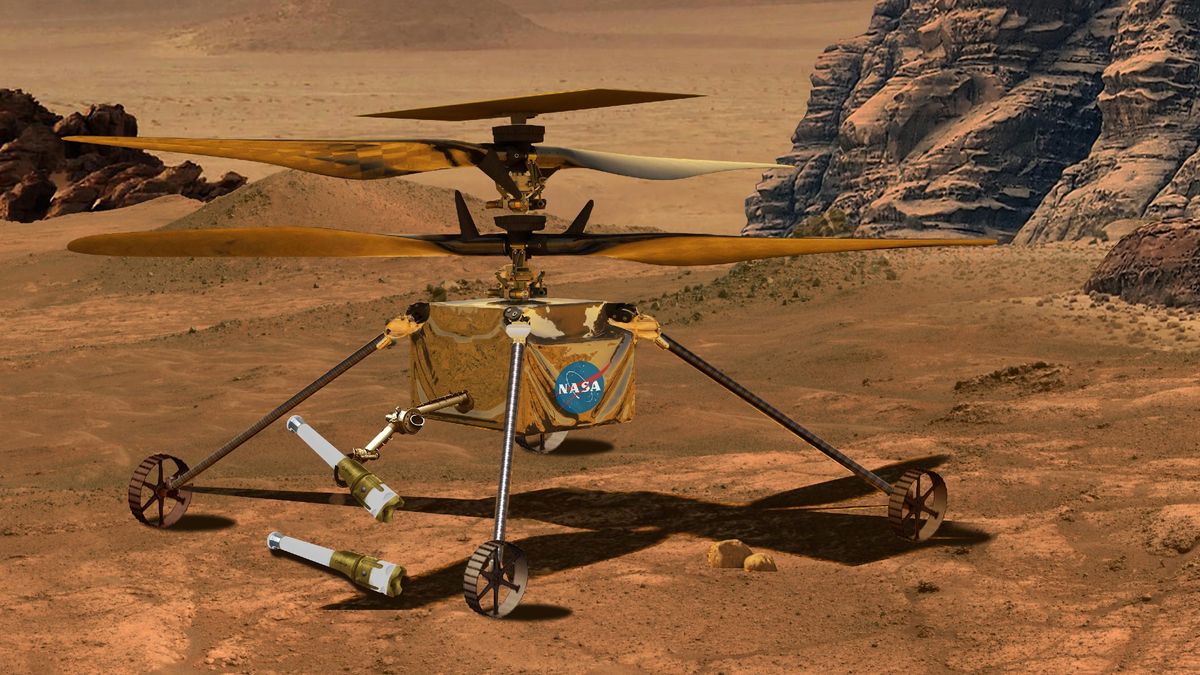

The basic design of a Mars helicopter is backed up by the dozens of flights NASA's Ingenuity has made.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Forgotten Equation Could Be Key In Recycling CO2 - OilPrice.com
4/15/23 at 3:00am

Cornell University scientists have turned to an old electrochemical equation from 1903 to help manage atmospheric CO2 and convert it into useful products.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

Unearthed video footage from 2019 shows a pilot whale expelling its placenta in Yell Sound, Shetland.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Scientists Unveil New, Improved 'Skinny Donut' Black Hole Image - NDTV
4/15/23 at 3:00am

NDTV.com: India, Business, Bollywood, Cricket, Video and Breaking News
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Direct imaging and astrometric detection of a gas giant planet orbiting an accelerating star - Science
4/15/23 at 3:01pm
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Viewed by
You are the first to view
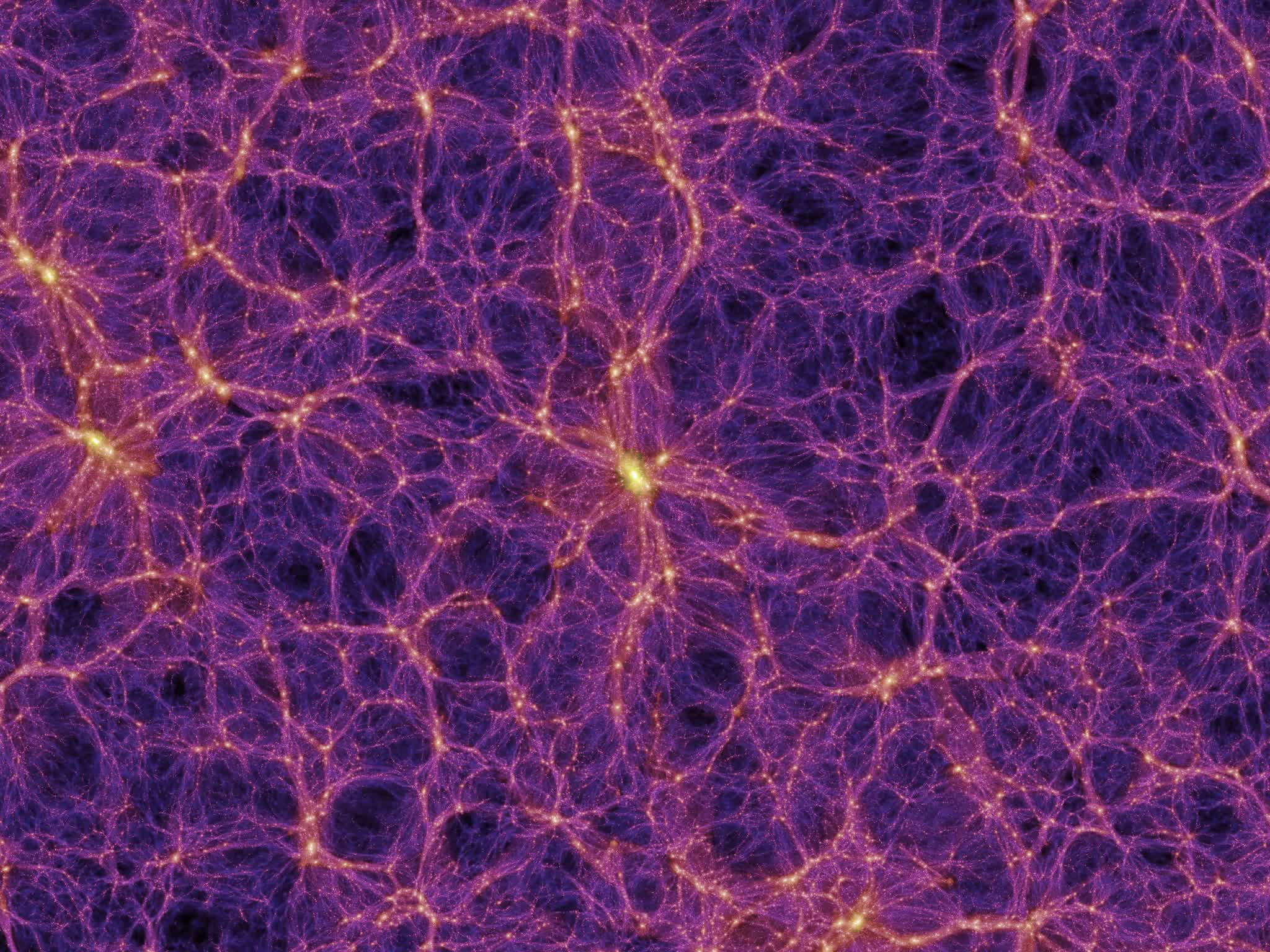

An international team of over 160 astronomers used the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) to shed new light on the invisible dark matter accounting for around 85 percent...
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Wobbling star found in Gaia-Hipparcos data confirmed to host exoplanet - European Space Agency
4/15/23 at 3:00am
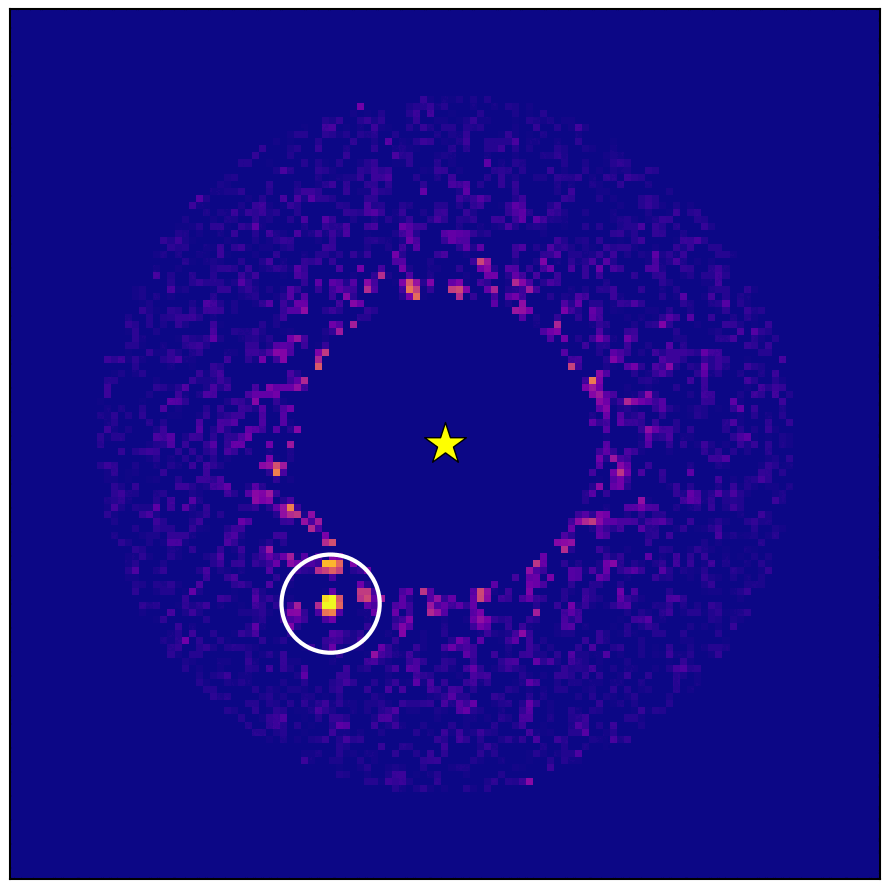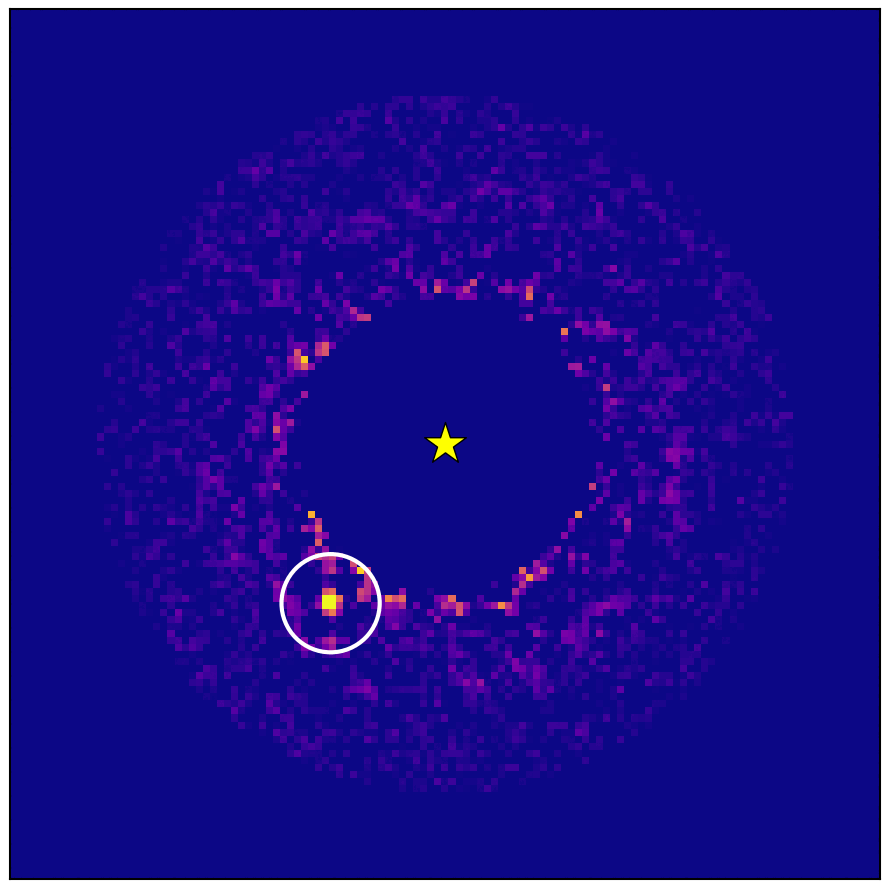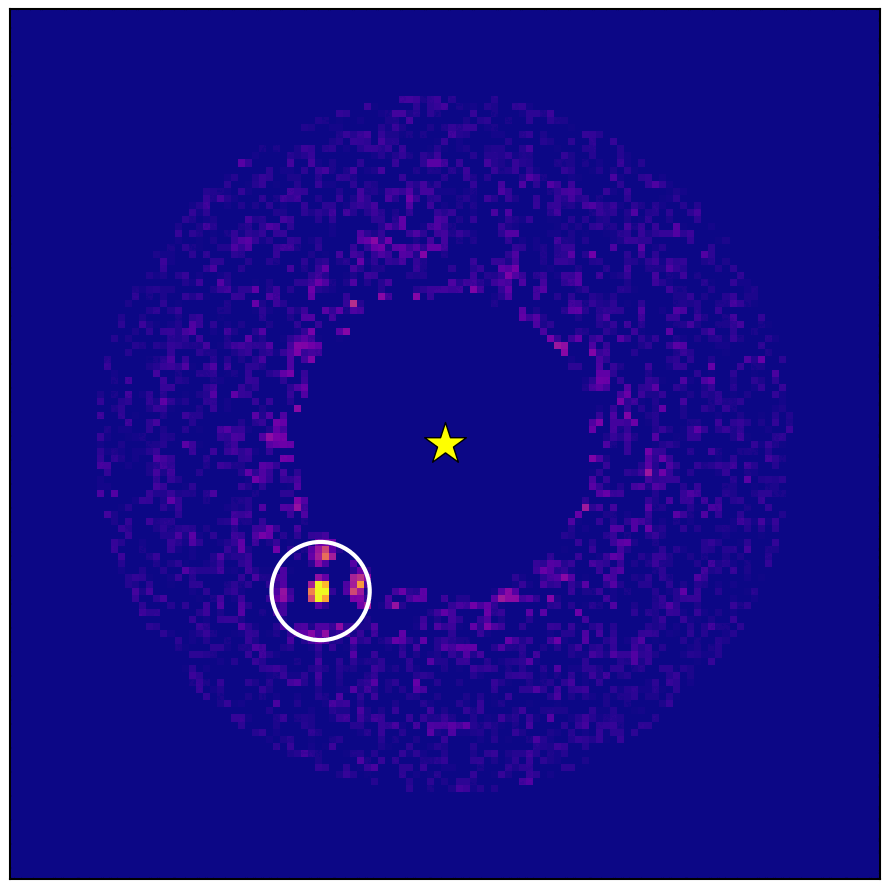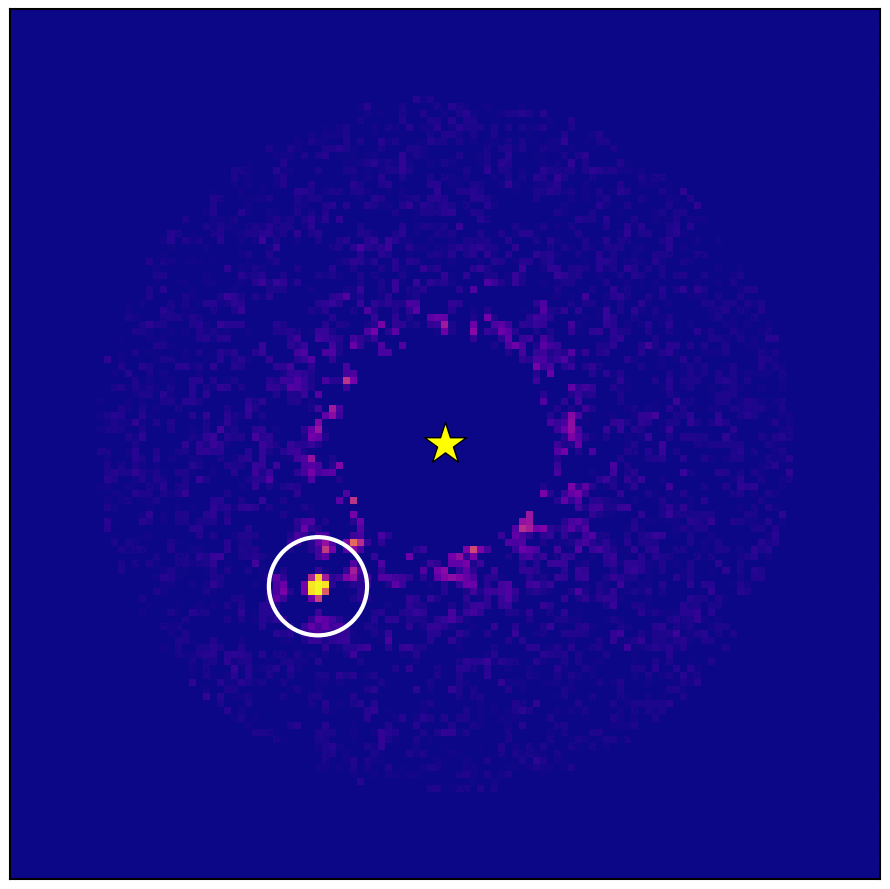
Data from ESA’s star-mapping Gaia spacecraft has allowed astronomers to image a gigantic exoplanet using Japan's Subaru Telescope. This world is the first confirmed exoplanet found by Gaia’s ability to sense the gravitational tug or ‘wobble’ a planet induces …
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Bats are an evolutionary mystery. This fossil could fill in a piece of the puzzle - CNN
4/15/23 at 3:00am

Two 52 million-year-old bat skeletons discovered in an ancient lake bed are the oldest bat fossils ever found, and they reveal a new species of flying mammal.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Wooded grasslands flourished in Africa 21 million years ago – new research forces a rethink of ape evolution - The Conversation
4/15/23 at 3:01pm
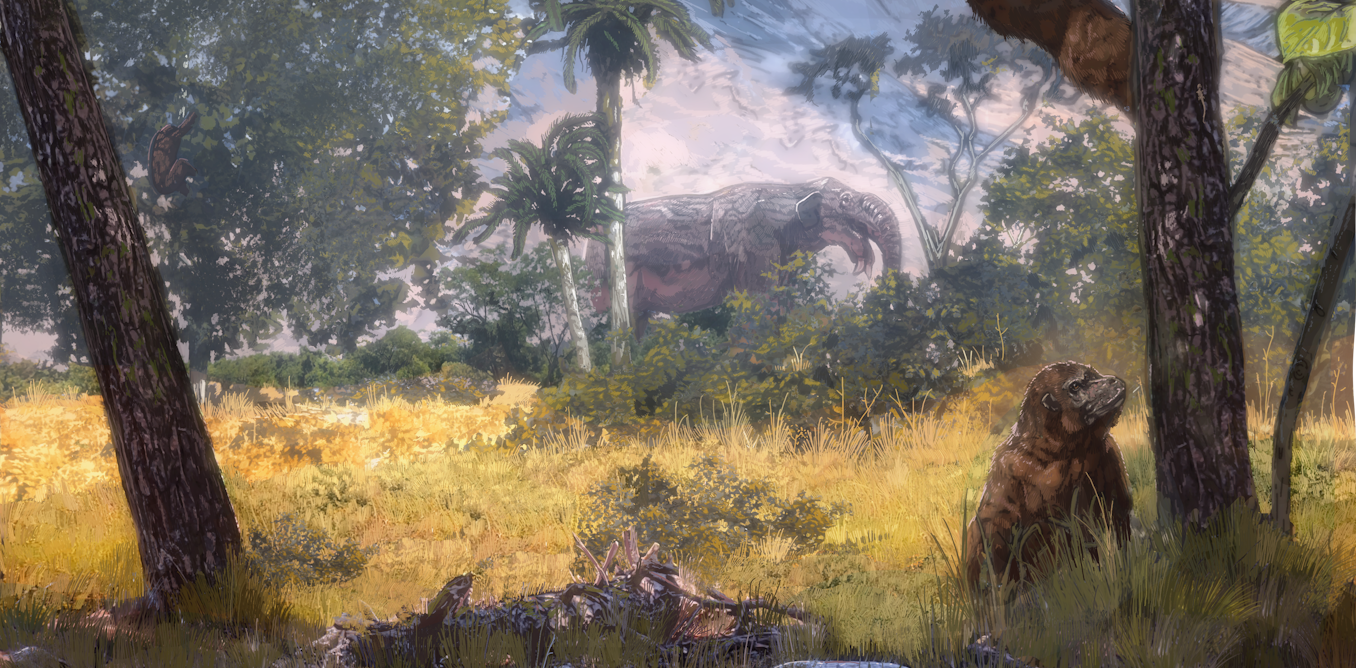

Contrary to the idea that apes evolved their upright posture to reach for fruit in the forest canopy, the earliest known ape with this stature, Morotopithecus, lived in more open grassy environments.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
One Brain, Multiple and Simultaneous Alternative Decision Strategies - Neuroscience News
4/15/23 at 3:00am

When it comes to decision-making, rather than committing to a single strategy, the brain computes multiple decision strategies simultaneously.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Apes may have evolved upright stature for leaves, not fruit, in open woodland habitats - Phys.org
4/15/23 at 3:00am

Anthropologists have long thought that our ape ancestors evolved an upright torso in order to pick fruit in forests, but new research from the University of Michigan suggests a life in open woodlands and a diet that included leaves drove apes' upright stature.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Researchers discover tiny galaxy with big star power using James Webb telescope - Phys.org
4/15/23 at 3:01pm

Using first-of-their-kind observations from the James Webb Space Telescope, a University of Minnesota Twin Cities-led team looked more than 13 billion years into the past to discover a unique, minuscule galaxy that generated new stars at an extremely high rat…
Viewed by
You are the first to view