49ers announce trade for Bryce Huff - NBC Sports
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Eagles move on from 2024 free-agent signing.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Iranian official says US nuclear proposal is ‘incoherent and disjointed,’ as sources warn talks momentum is collapsing - CNN
6/4/25 at 1:07am

A senior Iranian official told CNN the new nuclear deal proposal presented to Tehran in recent days is “incoherent and disjointed,” as sources familiar with the progress of the talks said the momentum behind negotiations to secure a new deal appears to be col…
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Stock futures are little changed after S&P 500 kicks off June with a modest gain: Live updates - CNBC
6/4/25 at 1:07am

The three major stock averages started June trading on a positive note.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

Any type of aerobic exercise works for the improvements, study finds.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Once inevitable collision between Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies now seems less likely, astronomers say - CNN
6/4/25 at 1:07am

A collision between our Milky Way galaxy and the neighboring Andromeda galaxy, long considered inevitable, may be in question, astronomers say.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
WhatsApp is finally getting usernames - 9to5Mac
6/4/25 at 1:07am

WhatsApp is gearing up to launch a long-awaited feature: usernames, so users can connect with others without sharing their actual phone number
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Homeland Security pulls down list of 'sanctuary' cities and counties after backlash - NPR
6/4/25 at 1:07am

The list included dozens of cities and counties that DHS said was in noncompliance with federal statutes and had come under intense criticism from some mayors and law enforcement.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
U.S. health officials have changed their advice to international travelers about measles, saying Americans should be vaccinated against the disease no matter where they travel in the world. U.S. residents are recommended to get measles-mumps-rubella shots, an…
Viewed by
You are the first to view

For the first time, OpenAI's Sora video generator will be available for free as it comes to the Microsoft Bing app.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Democrat announces run against Joni Ernst after ‘we’re all going to die’ comments - Politico
6/4/25 at 1:07am

State Rep. J.D. Scholten, who once challenged former Iowa Rep. Steve King, plans to launch his campaign on Monday.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

NYC's summer stargazing seasons begins with meteor showers and Pedro Pascal.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
'Strawberry Moon' 2025: June's full moon is about to break an annual record - Live Science
6/4/25 at 1:07am
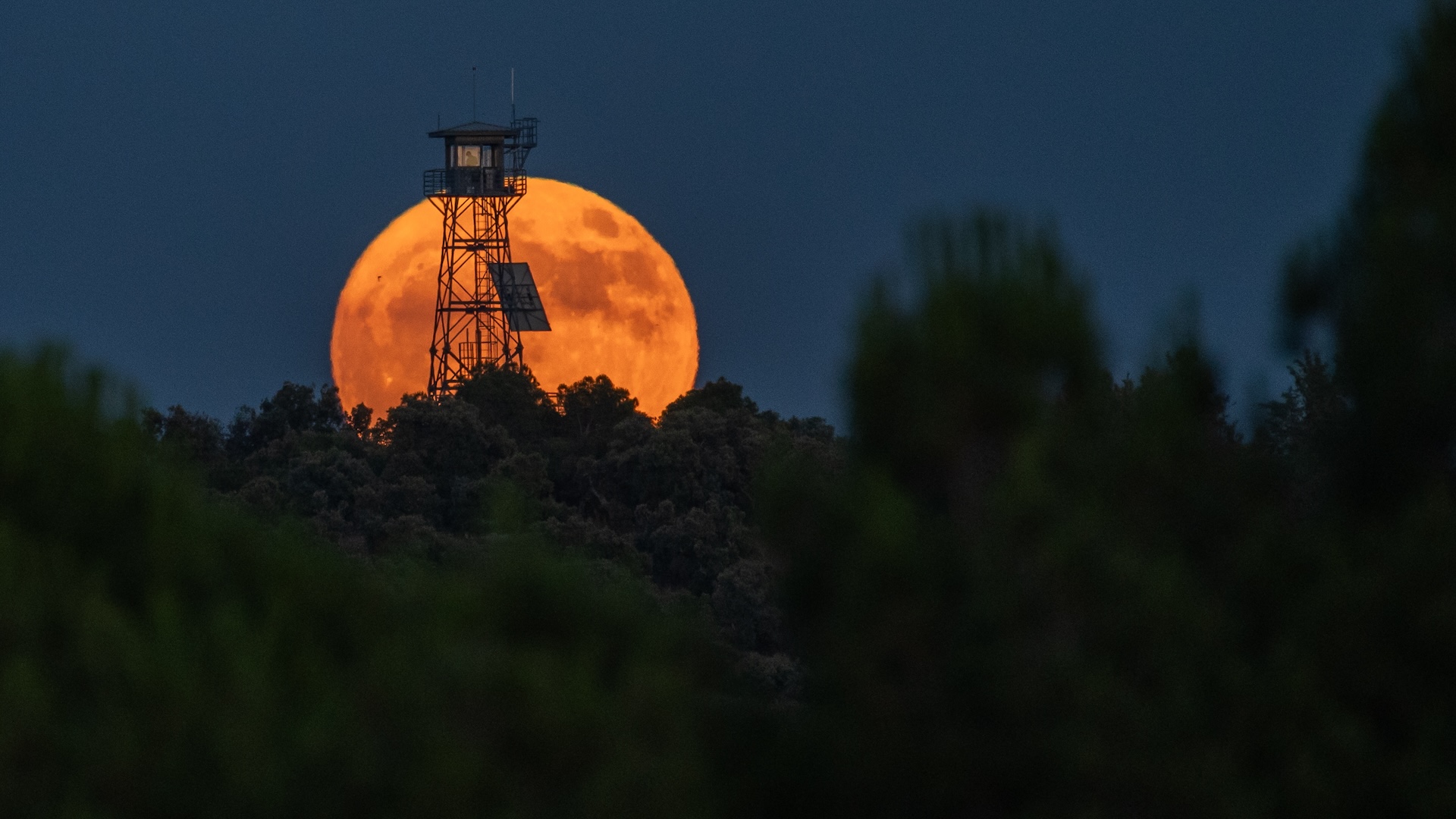

June's full 'Strawberry Moon' will be at its fullest on Wednesday, June 11, but the best time to see it will be at dusk on Tuesday, June 10.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

Salesforce has quietly snapped up Moonhub, a startup building AI to vet and hire talent. The terms of the deal weren't disclosed.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
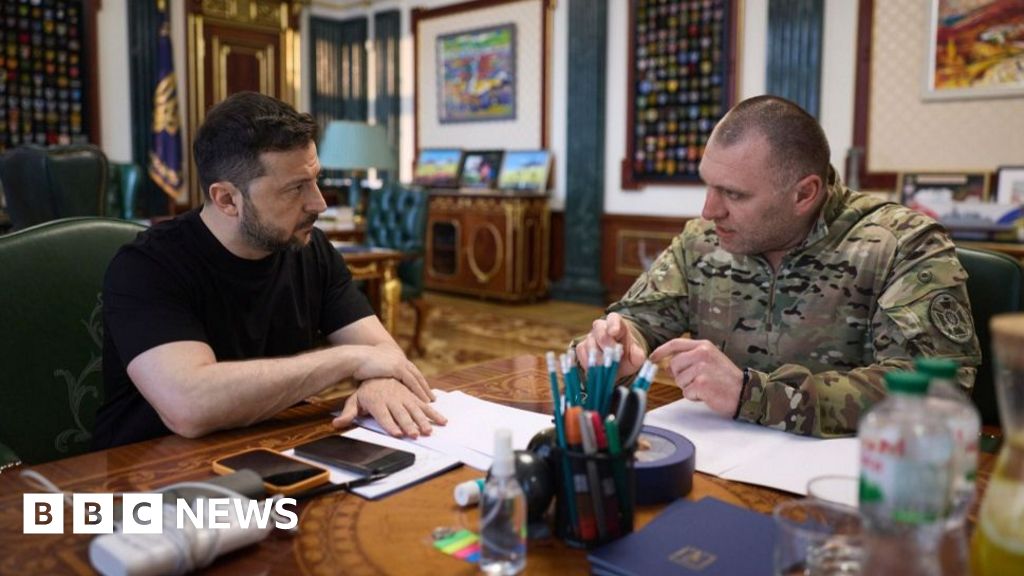

On 1 June, more than 100 Ukrainian drones struck strategic targets deep into Russia in an elaborate and audacious operation.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Poland election: Tusk to ask for a vote of confidence - dw.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Poland's Prime Minister Donald Tusk said he will request a vote of confidence in the near future. His centrist government suffered a setback after conservative nationalist Karol Nawrocki won the presidential election.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
#7 Lady Vols Drop Semifinal Matchup vs. #6 Texas, 2-0 - University of Tennessee Athletics
6/4/25 at 1:07am

No. 7 Tennessee's season came to an end Monday afternoon, falling to sixth-ranked Texas, 2-0, in the semifinals of the Women's College World Series.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Supreme Court denies challenges to bans on assault-style weapons and high-capacity magazines - NBC News
6/4/25 at 1:07am
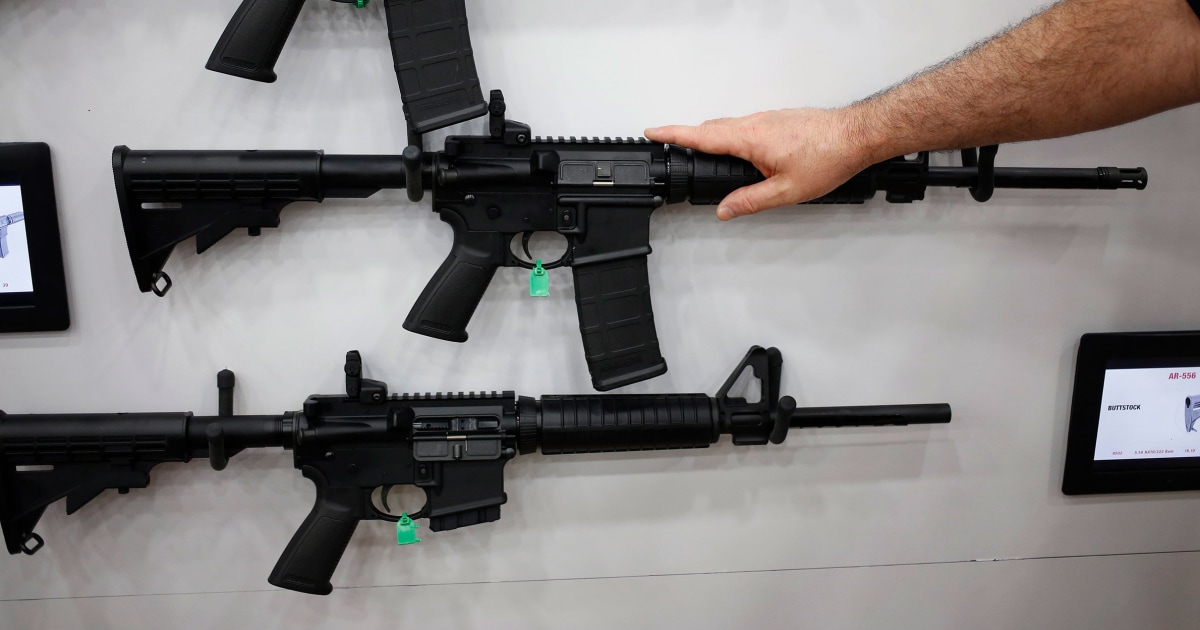

WASHINGTON — The Supreme Court on Monday declined to hear two major gun cases challenging a Maryland law that bans assault-style weapons, including the AR-15 semiautomatic rifle that has been used in high-profile mass shootings, and a Rhode Island restriction…
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Britain gets a defense boost aimed at sending a message to Russia, and to Trump - AP News
6/4/25 at 1:07am
The U.K. will build new nuclear-powered attack submarines and create an army ready to fight a war in Europe as part of a boost to military spending. It's designed to send a message to Moscow — and Washington. The government announced the moves Monday in respo…
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Shhh. Republicans are trying to repeal Obamacare again. Sort of. - The Washington Post
6/4/25 at 1:07am

They’re not branding it an Obamacare repeal this time around, but congressional Republicans are pursuing cuts to programs that are part of the 15-year-old health-care law.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
JoJo Siwa goes public about finding love with Chris Hughes on ‘Celebrity Big Brother’ - CNN
6/4/25 at 1:07am

There’s been a lot of conversation over the years about JoJo Siwa’s romantic relationships and now she’s added a new chapter.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

WWDC 2025 is just one week away, with Apple's opening keynote scheduled to begin on Monday, June 9 at 10 a.m. Pacific Time. Ahead of the annual...
Viewed by
You are the first to view
2025 NBA Mock Draft: VJ Edgecombe moves up to the No. 4 pick, Kon Knueppel falls out of top five - CBS Sports
6/4/25 at 1:07am
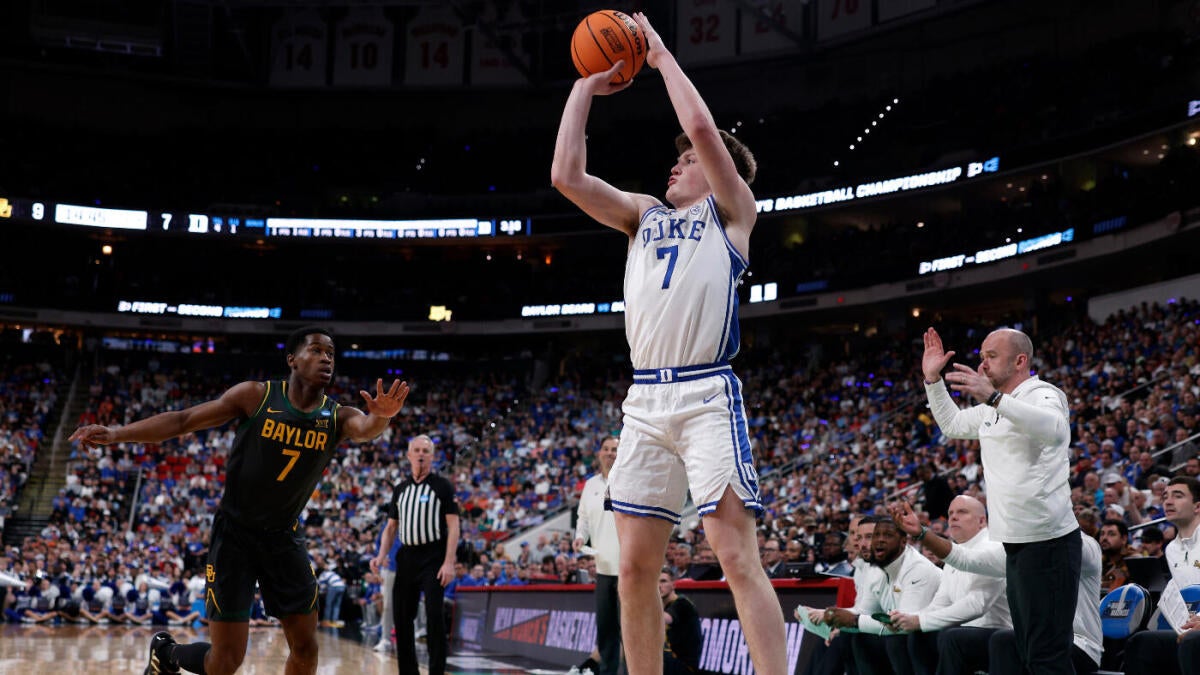

There is some shuffling in Kyle Boone's latest draft projections following the deadline for players to withdraw and return to school
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Family sues pharmacy, drug 'middleman' after price hike leads to son’s fatal asthma attack - NBC News
6/4/25 at 1:07am
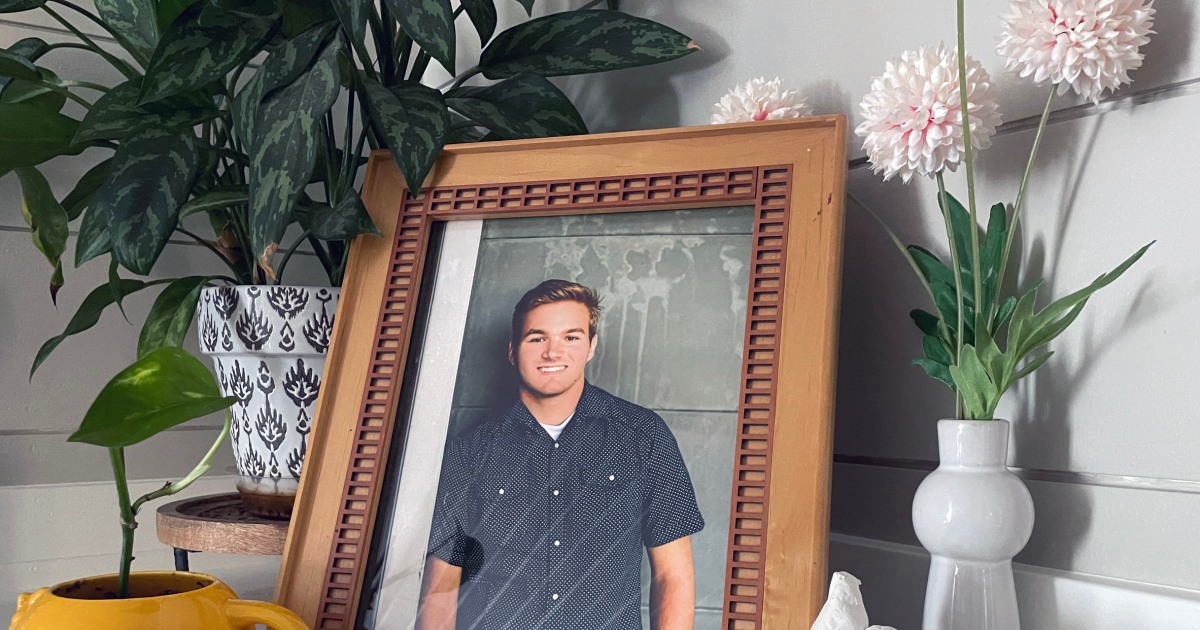

Cole Schmidtknecht, 22, had insurance but couldn’t afford to refill his asthma inhaler after the cost jumped from $70 to more than $500 at his pharmacy.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
A new study has uncovered a surprising culprit in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease: the immune molecule STING.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
How Cocaine Hijacks the Brain - Neuroscience News
6/4/25 at 1:07am

In a groundbreaking study, researchers have engineered fruit flies that voluntarily consume cocaine, creating the first fly model for cocaine addiction.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

A new study suggests that food quality matters more for heart health than cutting fat or carbs. A balanced diet with high quality, unprocessed foods is best for your heart.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

There are steps you can take to help address tingling and numbness in hands and feet caused by nerve pain.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

A fossilized stomach stone dating back 150 million years has been found on England’s Jurassic Coast, offering a rare glimpse into the digestive habits of ancient marine reptiles.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Minnesota confirms 2 new measles cases, including exposure at Mall of America - kare11.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am
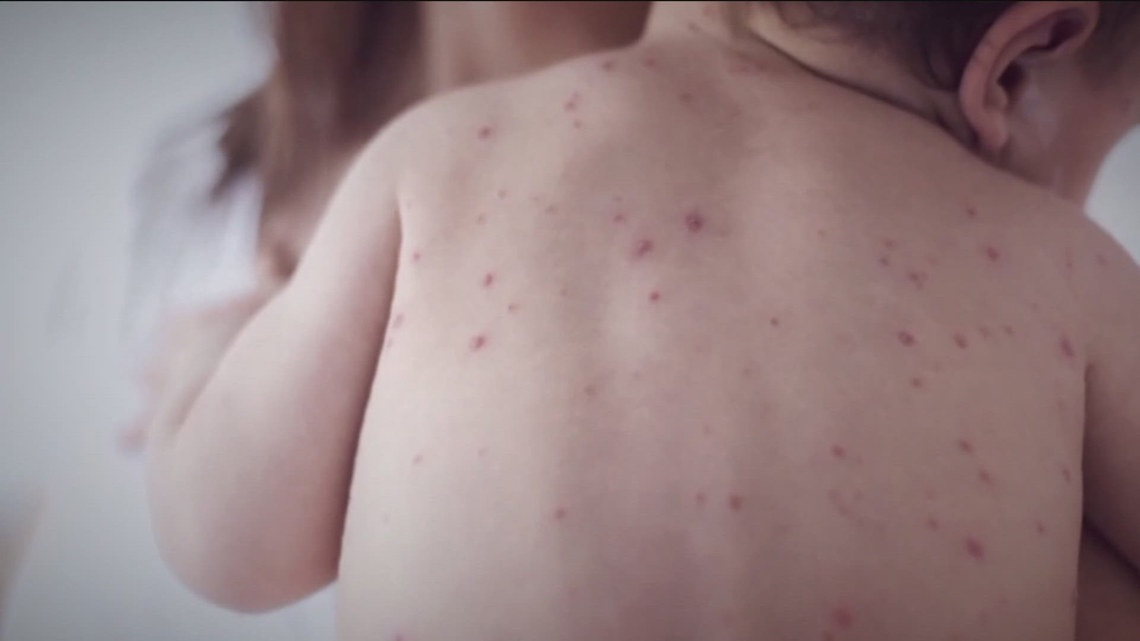
Minnesota health officials are alerting the public after a child with measles visited the Mall of America while infected.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
AI Cracks Mars Mystery: 500,000 Streaks Solved Without a Drop of Water - SciTechDaily
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Strange, dark streaks on Martian slopes that once hinted at flowing water are now believed to be dry dust slides, revealed through AI analysis of nearly 500,000 features.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
The #1 Breakfast to Eat to Support Your Metabolism, According to Dietitians - EatingWell
6/4/25 at 1:07am
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/The-1-Breakfast-to-Eat-to-Support-Your-Metabolism-e3f9ba97f0de4e89aa5162f8de5cc64c.jpg)
Spinach & Egg Scramble with Raspberries is an easy and nutritious start to your day. Dietitians explain why it's the best breakfast to support your metabolism.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
The workout supplement becoming more popular outside the gym - WTOP
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Creatine gives muscles extra energy, including your brain. Traditionally, supplements allow athletes the ability to do more exercise and add lean muscle mass.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Inhibitory Neurons May Hold the Key to Spatial Learning and Memory - Neuroscience News
6/4/25 at 1:07am
A new study explores how the brain quickly learns and remembers important locations by focusing not on excitatory neurons, but on inhibitory ones called parvalbumin interneurons (PVs).
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Study links preteen physical activity with better mental health later - The Washington Post
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Participating in organized sports at age 11 correlated with lower risks of mental health diagnoses for girls and boys, the researchers wrote.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
The #1 Snack for Better Gut Health, Recommended by a Gastroenterologist - EatingWell
6/4/25 at 1:07am
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/The-1-Snack-for-Gut-Health-Recommended-by-Gastroenterologists-878a0bb923f24ad3aea494be75497a2f.jpg)
Looking to improve your gut health? Read on to discover the best gastroenterologist-recommended plant-based snack to add to your day.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
This 1 Kitchen Tool Can Help You Cut Back On Oil & Calories, Dietitian Says - TODAY.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

When it comes to healthy eating, preparing meals at home is always a smart choice because you can control how much salt and oil you use.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
'The nutritional villain': BYU study says drinking sugar poses higher risk for diabetes than eating it - KSL News
6/4/25 at 1:07am

A study from Brigham Young University researchers found that consuming sugary drinks leads to a greater risk of developing Type 2 diabetes, and some forms of dietary sugar actually decrease the risk.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

“AI is rizzing them up in a very unhealthy way at the moment.”
Viewed by
You are the first to view

A Prior Lake artist living on borrowed time is dedicating the last of her healthy days helping to raise money and awareness for a cure.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Dear Doctor: What are the best ways to help my kidneys recover from nearly failing? - OregonLive.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

He wants to protect his kidneys and help them recover. Here are some tips.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
People’s Pharmacy: Aspirin thinking has changed for cardiovascular risks - OregonLive.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am
You recently wrote about a study regarding aspirin therapy for people with high Lp(a) levels. What is the current thinking?
Viewed by
You are the first to view
This Autoimmune Disease Has Ravaged Women For Centuries. New Treatments Could Finally Change That. - AOL.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Three new JAK inhibitor medications have hit the market in recent years to treat alopecia. While they don't cure it, they are changing people's lives.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Screen time and physical activity habits linked to adolescent stress and depression - PsyPost
6/4/25 at 1:07am

New research tracks over 500 Finnish children to explore how lifestyle habits affect teen mental health. The study suggests that more exercise and less screen time from a young age may reduce stress and depressive symptoms by age 15.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Gastroenterologist shares 5 early warning signs of poor liver health: From loss of appetite to dark patches on face - Hindustan Times
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Dr. Kavya reveals 6 subtle signs your liver may be struggling, from persistent fatigue to belly fat. Don’t ignore these crucial health signals. | Health
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Column | Nervous about using the bathroom at work? A gastroenterologist shares advice. - The Washington Post
6/4/25 at 1:07am

If you have to go, just go. Holding in your poop can put you at risk of hemorrhoids.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Three Seconds of Strength Training a Day Is All It Takes to Build Muscle Without Spending Hours at the Gym: Here’s How to Do It - The Daily Galaxy
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Just three seconds of daily exercise could change the way strength training works. A surprising study reveals unexpected results that challenge long-held fitness beliefs. This new approach might fit even the busiest schedules.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

Kindest Towns In America
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Not just genes: After 17 years of study, scientist discovers just 1 lifestyle change that could easily ad - Times of India
6/4/25 at 1:07am
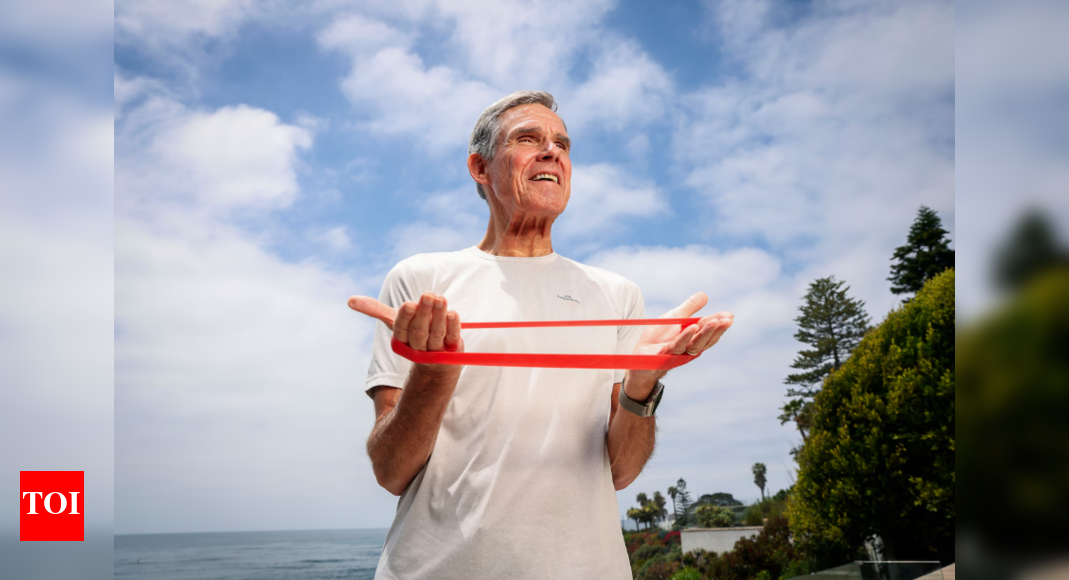

Dr. Eric Topol's research, spanning over seventeen years, debunked the myth of genetics as the primary determinant of healthy aging. One of the most i
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Authoritarianism in parents may hinder a key cognitive skill in their children - PsyPost
6/4/25 at 1:07am
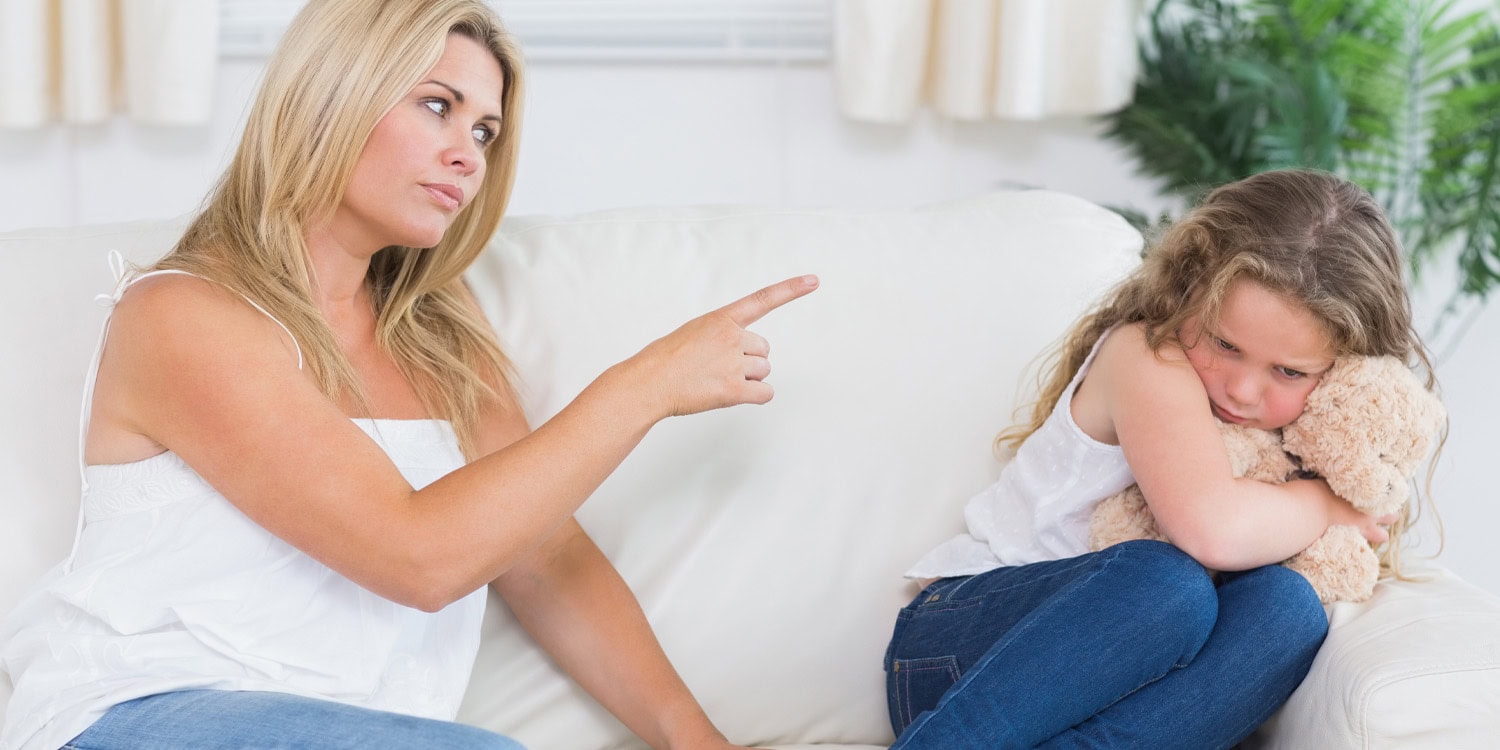

A new study suggests that mothers who favor social hierarchies and obedience to authority use less perspective-taking language with their children—especially when discussing people from different ethnic backgrounds. Their children also show weaker ability to …
Viewed by
You are the first to view
If You Can Perform These 5 Moves at 60, Your Body’s Decades Younger - Eat This Not That
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Experts say these 5 strength moves can keep your body decades younger—if you can do them at 60.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
How an unnoticed pregnancy complication almost ended a young Staten Island mom’s life - SILive.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am
"They told me that if I didn‘t come in sooner that I probably would have lost my life at any given moment."
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Mom Spotted a Growing Bump Near 3-Year-Old Daughter’s Eye. Then Came the Phone Call that Changed Their Lives (Exclusive) - AOL.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

In October 2024, Cameron Aldridge was diagnosed with B-cell lymphoma
Viewed by
You are the first to view
mRNA, once lauded as a scientific marvel, is now a government target - statnews.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

The sharp turnaround on mRNA vaccines shows the unprecedented rise of anti-vaccine activists to power
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Japanese Scientists Develop Artificial Blood Compatible With All Blood Types - Tokyo Weekender
6/4/25 at 1:07am
Japanese scientists have developed a new type of artificial blood that can be used in patients of any blood type.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

Research provides new insights into how the brain forms habits and explains why they can be so difficult to break. Neuroscientists at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre (SWC) at UCL have discovered that the brain uses two distinct systems to learn through trial an…
Viewed by
You are the first to view
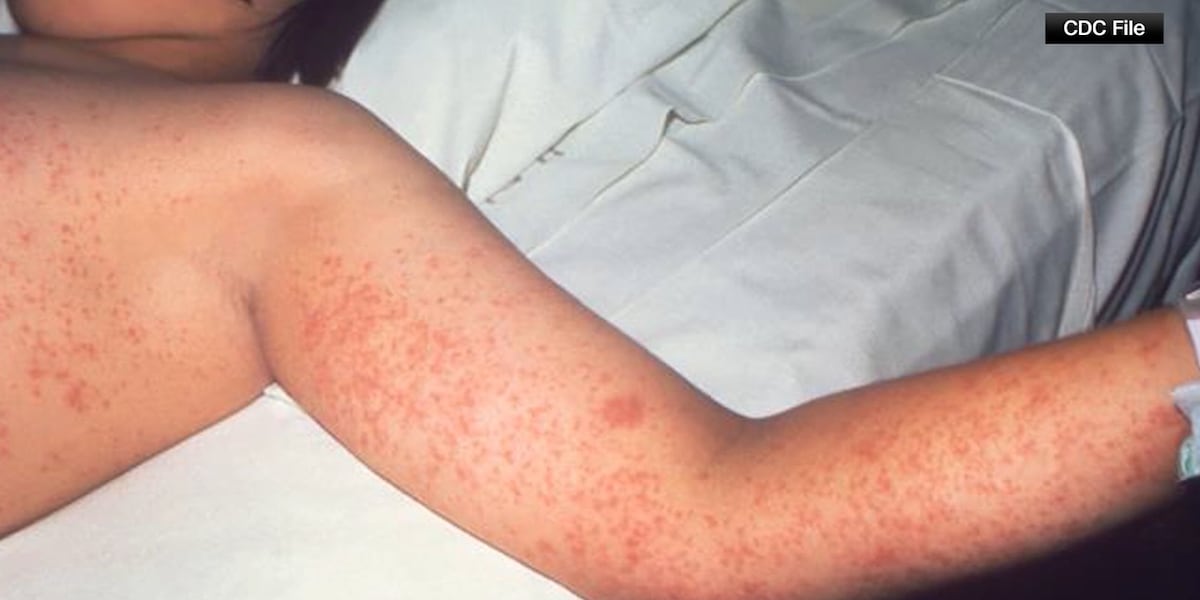
According to the Colorado Department of Public Health, and El Paso County Public Health, those residents were unvaccinated and are recovering at home.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
7-Day High-Protein Diabetes-Friendly Meal Plan to Help Build Muscle, Created by a Dietitian - EatingWell
6/4/25 at 1:07am
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/7-Day-High-Protein-Diabetes-Friendly-Meal-Plan-to-Help-Build-Muscle-Created-by-a-Dietitian-b73956544bff4e1ba86d04c73423df37.jpg)
Enjoy a week of high-protein, diabetes-friendly meals and snacks in this 7-day meal plan to build muscle, created by a dietitian.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Dog Disappears for 3 Years—What Happens When He Hears His Owner’s Voice Again Will Melt You - AOL.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

A family is reunited with his dog after a 3 year separation. The reaction of the dog is heartwarming
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Neuroscience breakthroughs: Surprising truths about memory revealed in 7 recent studies - PsyPost
6/4/25 at 1:07am
Memory is strange. It sharpens, fades, twists, and sometimes misleads. These seven recent studies uncover how emotion, stress, and biology shape what we remember—and what we forget.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Pharmacists warn drug shortage affecting cancer patients - BBC
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Some patients are skipping meals due to a shortage of Creon, says a pharmacy association.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Deadliest Creature On Earth Now In Wisconsin In Staggering Numbers - Duluth Country Radio
6/4/25 at 1:07am

These relentless creatures kill a whopping 725,000 humans each year and they are now in Wisconsin in staggering numbers.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
A new variant of COVID-19 may be driving up cases in some parts of the world, WHO says - Mother Lode's News - myMotherLode.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am
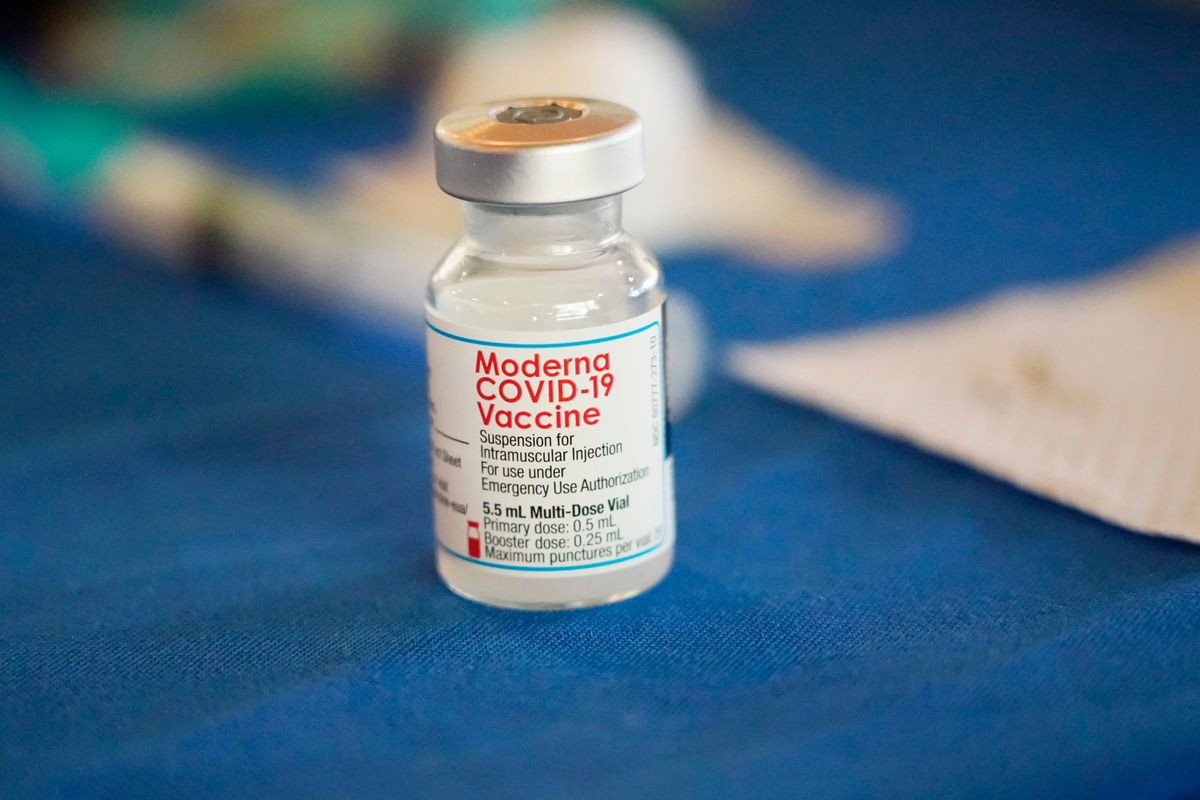
A new variant of COVID-19 is circulating in parts of the world and may be driving an increase in cases in the eastern Mediterranean, Southeast Asia and western Pacific regions.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
The Best Time to Take Vitamin D for Maximum Absorption, According to Health Experts - Yahoo
6/4/25 at 1:07am

A doctor and dietitian break down what to consider as you choose when to take your dose.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
The Silent Symptom Most People Don't Realize Could Be a Heart Issue, According to Cardiologists - Yahoo
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Cardiologists are getting loud about a sneaky red flag of heart issues.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
My Girlfriend Had a Legendary Sex Life Before Me. No One Will Let Me Forget It. - Slate Magazine
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Even years later, it's the talk of the town.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Can omega-6 fatty acids in nuts, vegetable oils lower heart disease and diabetes risk? - Medical News Today
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Following a diet higher in the omega-6 fatty acid linoleic acid may help support cardiometabolic health, and lower a person's risk for type 2 diabetes and heart disease, a new study indicates.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

The researchers assessed waves on the Colorado River in Texas, the Ocmulgee River in Georgia and the Yellowstone River in Montana.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

He just made two bad decisions on vaccines, and he made them in the worst way possible.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
T Cells Found Living in Healthy Brains - Neuroscience News
6/4/25 at 1:07am
Contrary to long-standing beliefs, T cells—key immune cells—have been discovered in the healthy brains of both mice and humans.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Drugs that boost the body’s immune system to fight disease are showing promise in treating a variety of cancers in earlier stages, a development primed to expand their use and transform care for stubborn diseases like gastric and colon cancer.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Grandfather Diagnosed With Stage Four Lung Cancer Becomes Free of Disease After Immunotherapy - Good News Network
6/4/25 at 1:07am

A grandad diagnosed with stage 4 lung cancer–one of the deadliest—has become disease-free after being treated with an immunotherapy drug.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Woman who had stroke on flight saved by quick landing in Houston - Houston Chronicle
6/4/25 at 1:07am
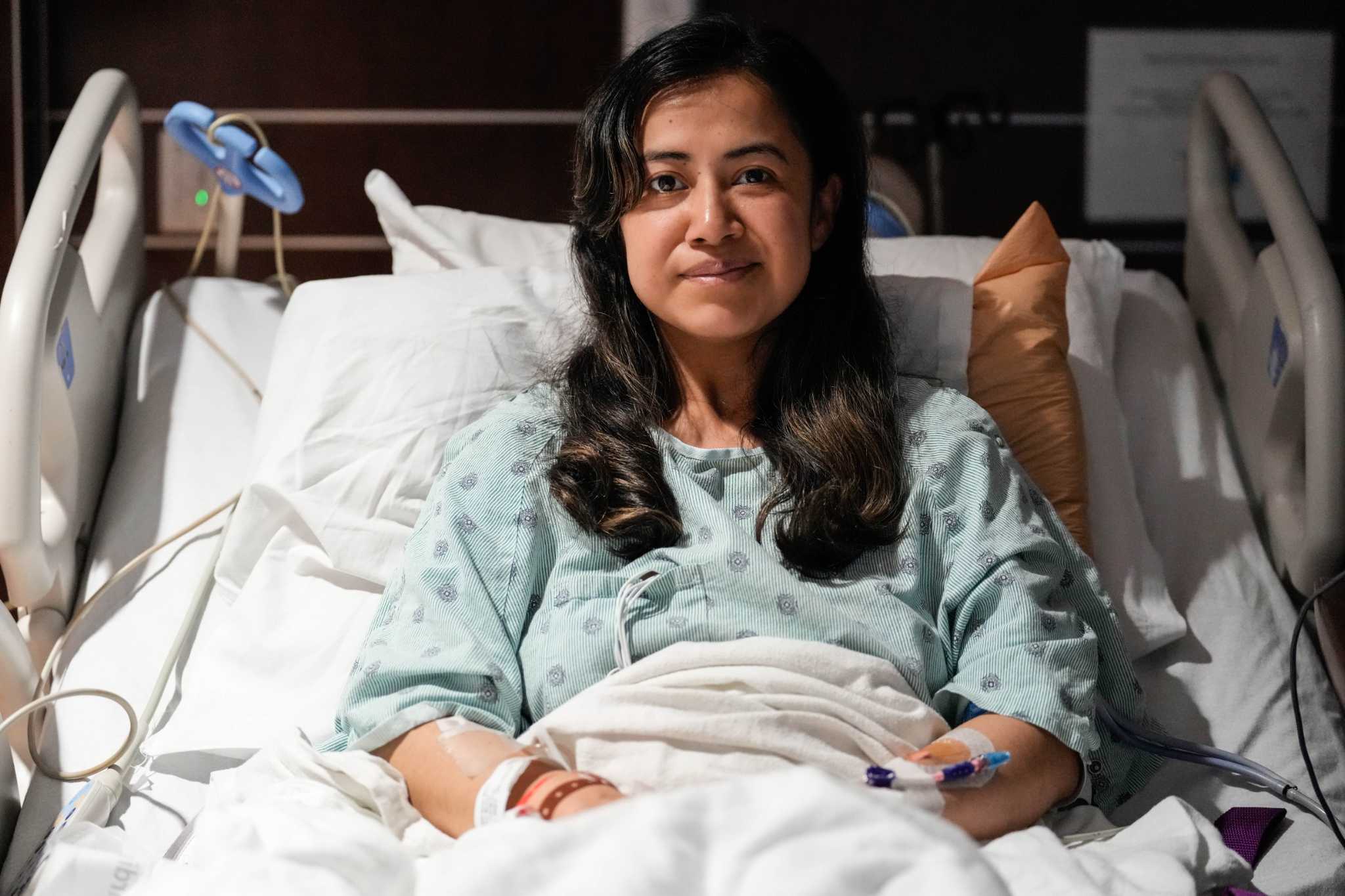

A woman had a stroke on a flight from Turkey to Mexico, but avoided permanent brain damage after a doctor persuaded the flight crew to land in Houston.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
According to Scientists, This Is the Most Important Thing To Restore Your Gut Health - SciTechDaily
6/4/25 at 1:07am

A healthy diet is more effective than fecal transplants at restoring and protecting the gut microbiome. Trillions of microbes live in your body. Far from being harmful, most of these microorganisms form a diverse and vital community that supports digestion, b…
Viewed by
You are the first to view
'Orthorexia' Is More And More Common. Here's What You Should Know About It. - HuffPost
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Social media pressures only makes this condition more prevalent.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
This Is How To Make Your Brain Act 4 Years Younger, According To Science - MindBodyGreen
6/4/25 at 1:07am

We're turning back the clock!
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Turmeric, celebrated for its health benefits, faces scrutiny due to reports of liver damage linked to supplements, as highlighted by the Daily Mail. R
Viewed by
You are the first to view

Migraines are one of the most complex neurological disorders. What is the science behind the latest hack?
Viewed by
You are the first to view

New research suggests that vitamin D supplements may slow biological aging by protecting telomeres, the DNA caps linked to age-related disease and cellular h...
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Viewed by
You are the first to view
In a remarkable scientific discovery, researchers have unearthed a plant fossil that defies conventional botanical classification. This 47-million-year-old specimen, named Othniophyton elongatum, has left paleobotanists puzzled as it appears to belong to no k…
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Scientists identify time and location of first humans who made tools and harpoons out of whale bones - Earth.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Paleolithic humans used whale bones as tools 20,000 years ago, the earliest evidence of marine tool-making discovered.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Scientists find a boulder weighing 2,645,547 pounds that was washed inland by an enormous tsunami - Earth.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

A massive, cliff-top boulder in Tonga reveals a 7,000-year-old mega tsunami, offering new insights for coastal hazard planning.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

Solar storms are heating up Earth’s atmosphere, pushing satellites like Starlink to return earlier than expected.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Discover Why These 2025 Milky Way Photos Are Shaking the Astrophotography World - The Daily Galaxy
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Stunning photos reveal the Milky Way like never before—captured from Earth’s darkest places and even from space itself.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Discovery of 100-million-year-old dinosaur eggs reveals life in Jurassic America - Earth.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Paleontologists assumed just one dinosaur egg type lay buried in Utah's Cedar Mountain Formation. Then they hit the jackpot.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Private Japanese spacecraft aims to land in the moon's 'Sea of Cold' this week - Space
6/4/25 at 1:07am
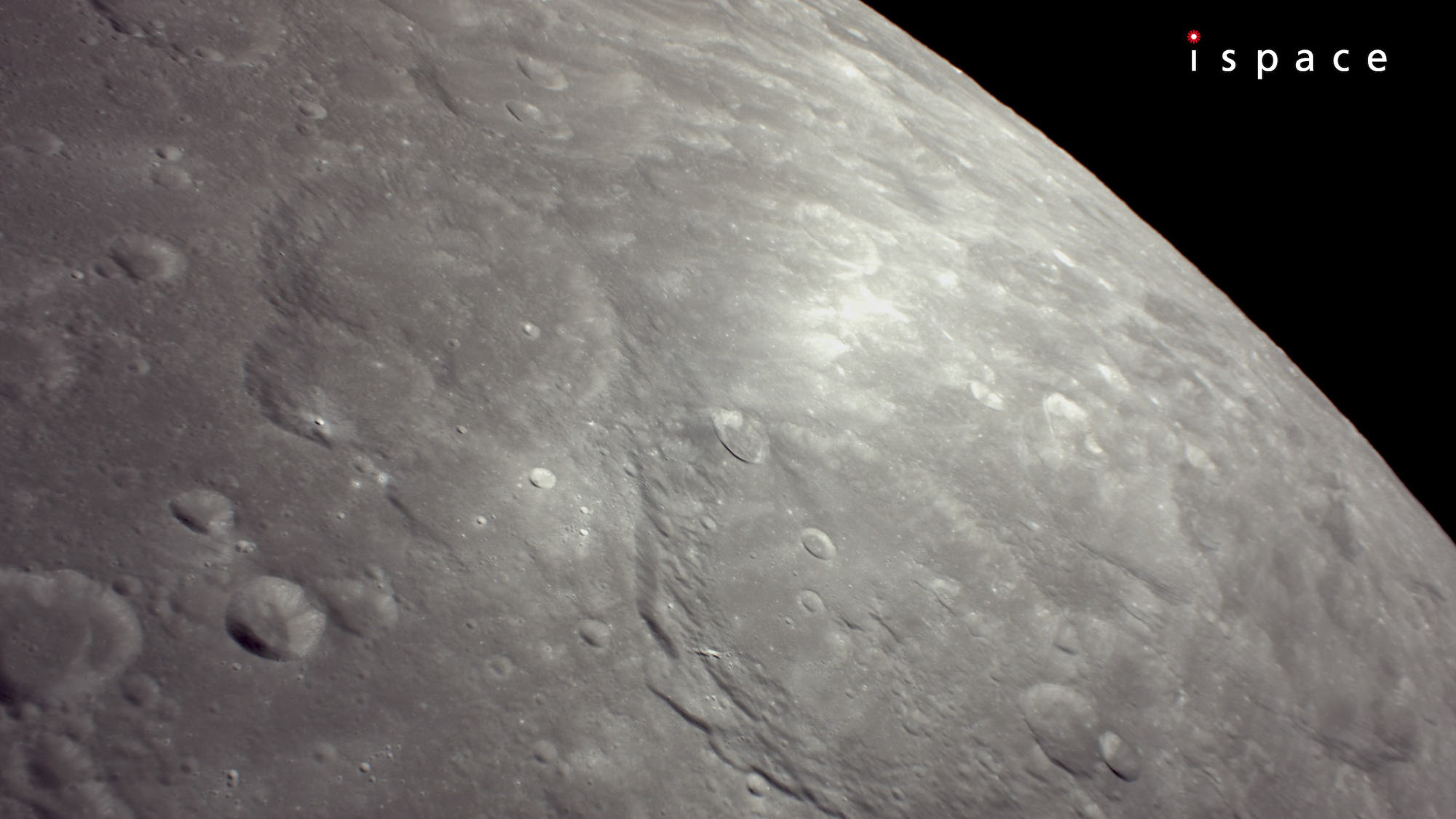

Touchdown is scheduled for 3:24 p.m. ET on Thursday (June 5).
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Ultra-thin lenses halve incident wavelength to make infrared light visible - Phys.org
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Physicists at ETH Zurich have developed a lens that can transform infrared light into visible light by halving the wavelength of incident light. The study is published in Advanced Materials.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Scientists develop an advanced method to better confine energetic particles in fusion reactors, significantly boosting stellarator efficiency.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
What Is the “Dogxim”, the World’s Only Unique Hybrid Animal That Has Scientists Deeply Concerned - Indian Defence Review
6/4/25 at 1:07am

ChatGPT a dit : A mysterious animal discovered in southern Brazil is unlike anything seen before — part wild fox, part domestic dog. Scientists are baffled by its unusual traits and genetic makeup.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Don't miss the half-lit first quarter moon rise tonight — Here's what to look for - Space
6/4/25 at 1:07am
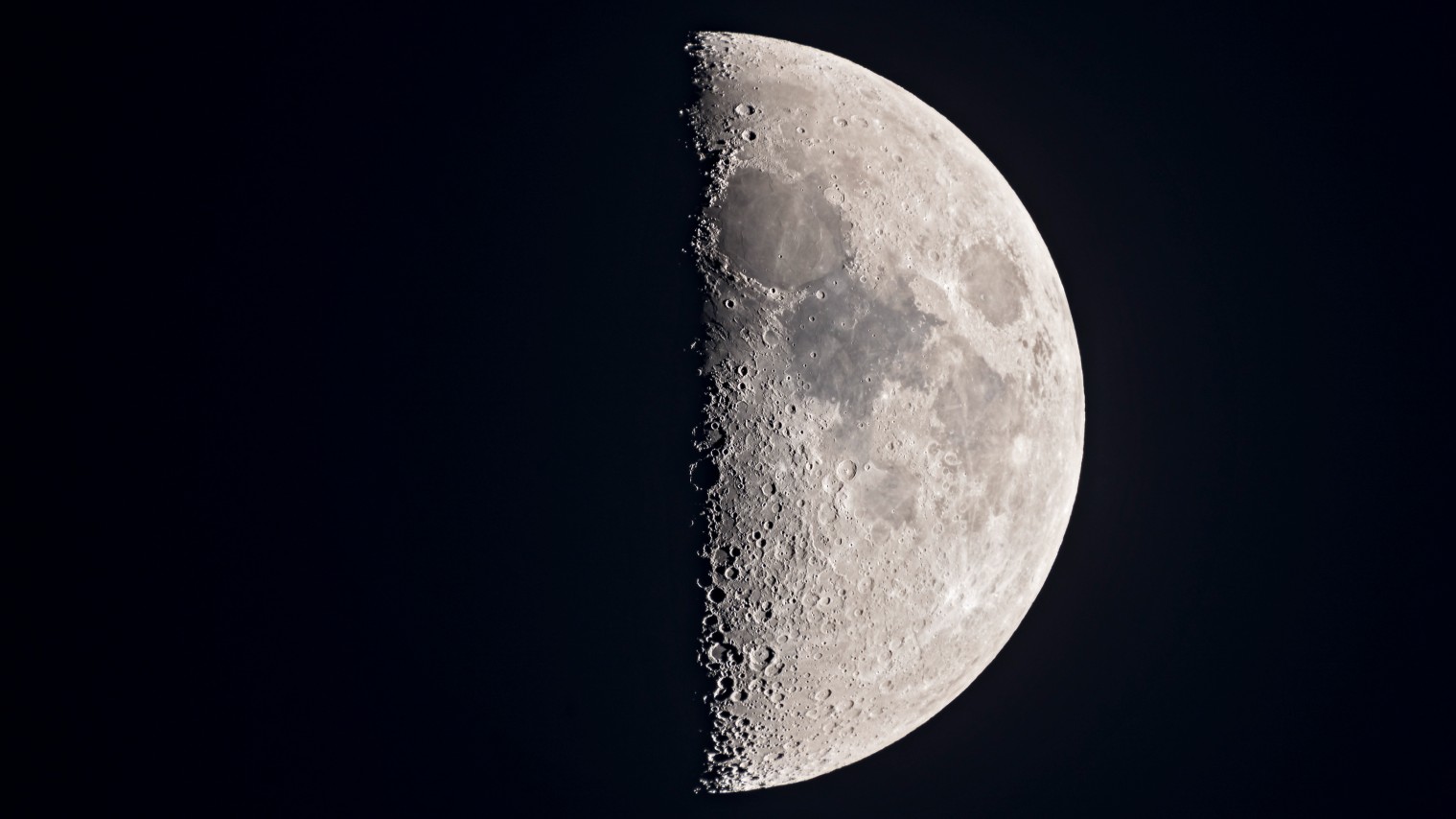

The first quarter moon is the perfect opportunity to explore shadowed craters lining the terminator.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Earth’s oldest living creature unearthed—dating back 700 million years - The Brighter Side of News
6/4/25 at 1:07am
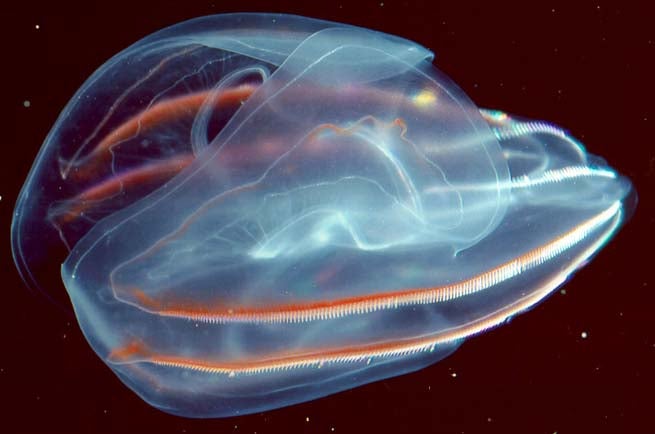

For over a century, scientists have wrestled with one of biology’s most fundamental mysteries: how the first animals evolved.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Turning the Red Planet green? It's time to take terraforming Mars seriously, scientists say - Space
6/4/25 at 1:07am
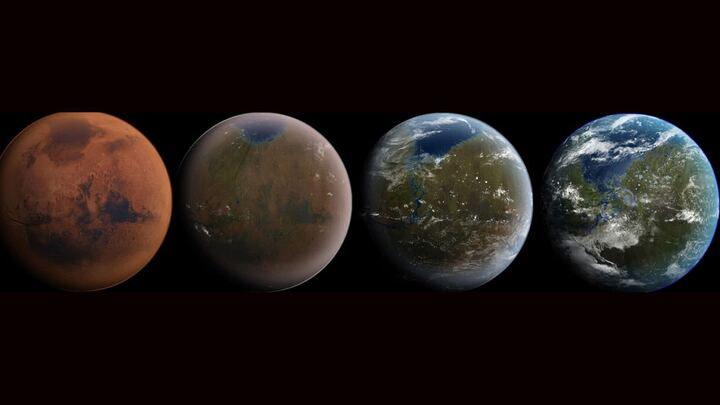

New research suggests that the idea of transforming the Red Planet might not be so far-fetched after all.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

Scientists analyzing an ultra-hot giant planet believe it was formed by absorbing lightweight gases like methane evaporating from tiny space pebbles, while being bombarded with large rocky objects.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
How are you able to read words without vowels? - Live Science
6/4/25 at 1:07am
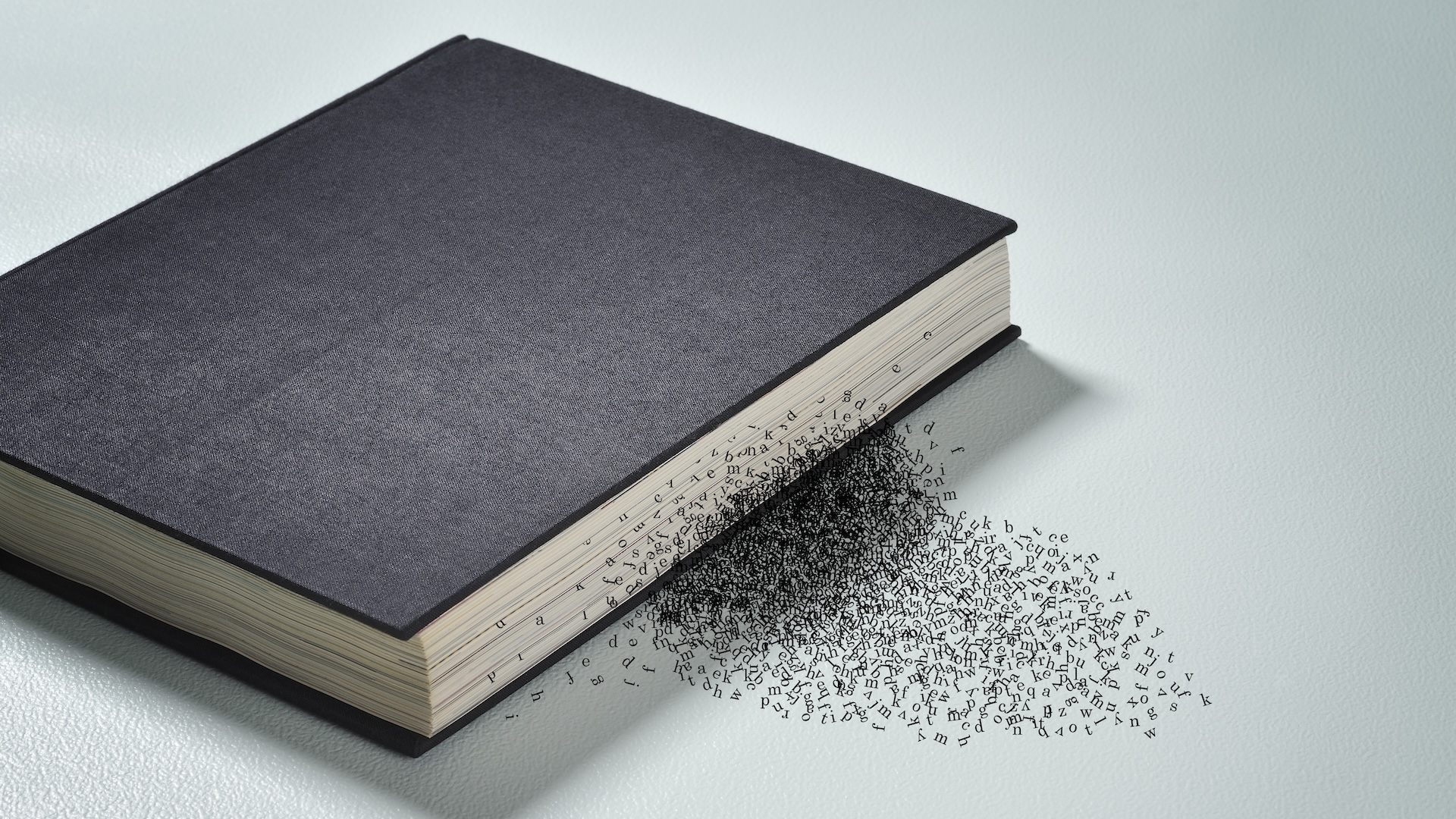

The human brain can make sense of sentences — even when the vowels are missing.
Viewed by
You are the first to view

The Galerie David Guiraud presents an exhibition on the theme of deep space, that is, the nebulae and galaxies of our universe that have […]
Viewed by
You are the first to view
MIT Breakthrough: Star-Shaped Brain Cells Could Be the Secret Behind Human Memory - SciTechDaily
6/4/25 at 1:07am
Astrocytes might be the brain’s secret memory engines — and a future blueprint for smarter AI.
Viewed by
You are the first to view
Archaeologists find what may be the first definitive proof that Neanderthals made artwork - Earth.com
6/4/25 at 1:07am

Neanderthals may have used a red pigment on a rock to shape what looks like art - a rendition of a facial figure from 43,000 years ago.
Viewed by
You are the first to view


